March 5, 2025
Jason N. Sheffield, J.D., National Director of Compliance
Part I: Nondiscrimination for Dependent Care Assistance Programs
Discrimination Prohibited in Favor of Highly Compensated Employees. Federal tax law imposes nondiscrimination requirements on dependent care assistance programs (“DCAPs”) to make sure that they do not discriminate in favor highly compensated employees (“HCEs”). If a DCAP is discriminatory, the benefits provided to HCEs will be taxable, but the non-HCEs’ benefits will not be affected. Discriminatory benefits under a DCAP are reported as wages in Box 1 of the HCE’s
Form W-2.
Definition of HCE. The definition of HCE is similar to the definition used to perform Internal Revenue Code (“IRC”) §401(k) testing and generally includes the group of employees who had compensation exceeding a specified dollar threshold for the preceding plan year (e.g., $155,000 if the preceding plan year is 2024, and $150,000 if the preceding plan year is 2023), and, if elected by the employer, was also in the “top-paid group” of employees (that is, the top 20 percent).
DCAP Nondiscrimination Tests. In order to avoid adverse consequences to the HCEs, a DCAP must satisfy the following nondiscrimination tests under IRC §129:
- The Eligibility Test;
- The Contributions and Benefits Test;
- Ownership Concentration Test; and
- The 55% Average Benefits Test.
Part II: Eligibility Test
Eligibility as to Participation. A DCAP must not discriminate in favor of HCEs as to eligibility to participate. This nondiscrimination test looks at whether there is a bona fide business reason for any exclusions and whether a sufficient percentage of non-HCEs are eligible to participate in the DCAP.
Eligibility Testing Process. The process for performing the Eligibility Test is as follows:

Part III: Contributions and Benefits Test
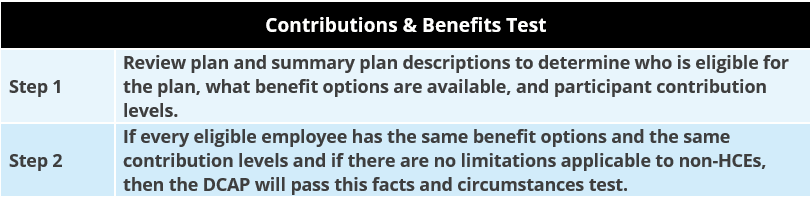
Eligibility as to Contributions & Benefits. A DCAP must not discriminate in favor of HCEs as to contributions and benefits received under the plan. This test considers whether HCEs and non-HCEs receive the same amount of employer contributions (if any) and whether they are entitled to the same amount of benefits from the DCAP.
Contributions & Benefits Testing Process. The process for performing the Contributions and Benefits Test is as follows:
Part IV: Ownership Concentration Test
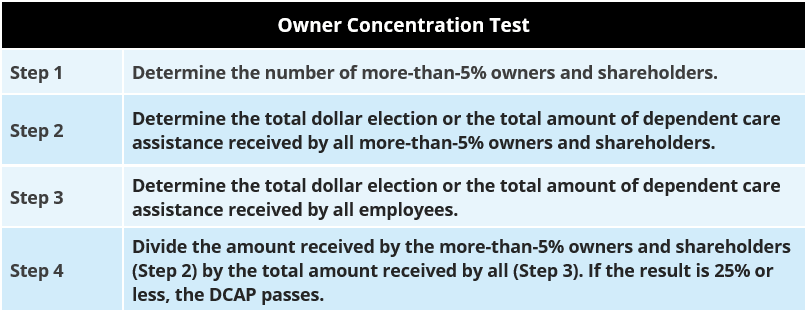
This nondiscrimination test looks at DCAP utilization to make sure that certain HCEs do not receive more than 25% of the total benefits provided by the DCAP. Not more than 25% of the amounts paid or incurred by the employer for dependent care assistance during the year may be provided for the class of individuals who are shareholders or owners, each of whom (on any day of the year) own more than 5% of the stock or of the capital or profits interest in the employer.
Owner Concentration Testing Process. The process for performing the Owner Concentration Test is as follows:
Part V: 55% Average Benefits Test
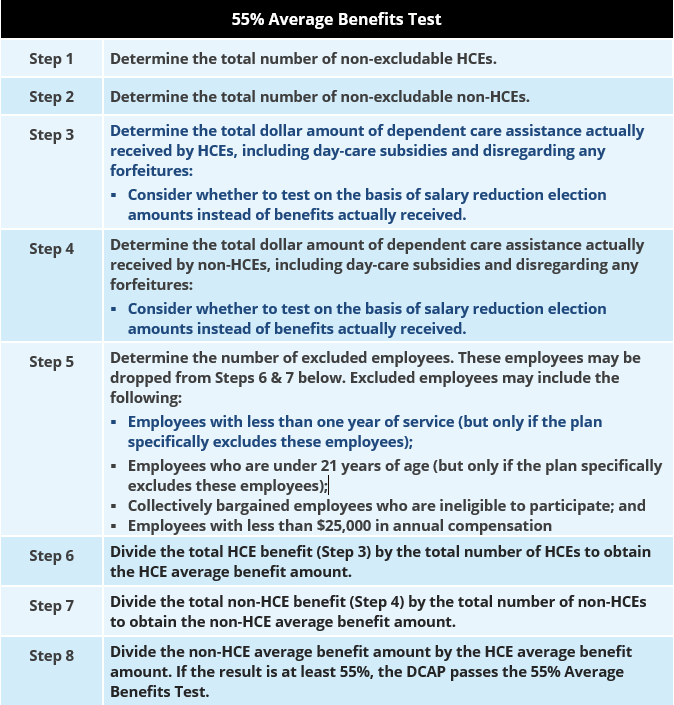
Benefits Provided to Non-HCEs. The average benefits provided to employees who are non-HCEs must be at least 55% of the average benefits provided to HCEs. This test is intended to ensure that HCEs do not disproportionately utilize the DCAP’s benefits.
55% Average Benefits Testing Process. The process for performing the 55% Average Benefits Test is as follows:
IRC §125 Testing Requirements. DCAPs that are offered as a qualified benefit under cafeteria plans are also subject the additional nondiscrimination testing requirements that apply to cafeteria plans under IRC §125.
Part VI: Questions & Additional Support
Additional Support
To obtain additional support for performance of these and other nondiscrimination related requirements, as mandated by the Internal Revenue Code, please reach out to your local service colleague or your client advisor. The Baldwin Group maintains an extensive suite of support solutions and advisory guidance capabilities respecting an employer plan sponsor’s performance of its IRS nondiscrimination related compliance assuredness activities. The Baldwin Regulatory Compliance Collaborative (the “BRCC”) also offers a carefully curated range of consultative and advisory support solutions related to the administration of US-based employee benefit plans, program, and other offerings.
For more information
We’re ready when you are. Get in touch and a friendly, knowledgeable Baldwin advisor is prepared to discuss your business or individual needs, ask a few questions to get the full picture, and make a plan to follow up.
This document is intended for general information purposes only and should not be construed as advice or opinions on any specific facts or circumstances. The content of this document is made available on an “as is” basis, without warranty of any kind. The Baldwin Insurance Group Holdings, LLC (“The Baldwin Group”), its affiliates, and subsidiaries do not guarantee that this information is, or can be relied on for, compliance with any law or regulation, assurance against preventable losses, or freedom from legal liability. This publication is not intended to be legal, underwriting, or any other type of professional advice. The Baldwin Group does not guarantee any particular outcome and makes no commitment to update any information herein or remove any items that are no longer accurate or complete. Furthermore, The Baldwin Group does not assume any liability to any person or organization for loss or damage caused by or resulting from any reliance placed on that content. Persons requiring advice should always consult an independent adviser.
The Baldwin Group offers insurance services through one or more of its insurance licensed entities. Each of the entities may be known by one or more of the logos displayed; all insurance commerce is only conducted through The Baldwin Group insurance licensed entities. This material is not an offer to sell insurance.






